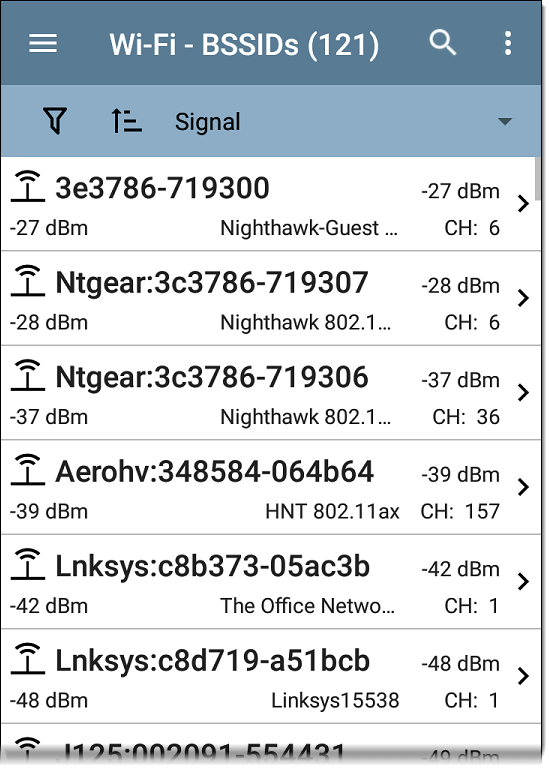
BSSIDs
The BSSIDs list screen shows the BSSID addresses discovered in your wireless environment.
You can Filter ![]() and Sort
and Sort ![]() the list to determine which BSSIDs are shown and their order. Refer to the Wi-Fi App List Screens topic if needed.
the list to determine which BSSIDs are shown and their order. Refer to the Wi-Fi App List Screens topic if needed.
By default, BSSIDs are ordered by signal strength, and each card shows the signal strength, SSID, and channel number on which the BSSID operates. The icons indicate different types of BSSID:
|
|
Single, transmitted |

|
Reduced neighbor report, transmitted |
|
|
Reduced neighbor report, non-transmitted |
|
|
Multiple, transmitted (6 GHz) |

|
Multiple, non-transmitted (6 GHz) |
Colors show the BSSID's status: black indicates normal status, yellow indicates a warning-level problem, and red indicates an error-level problem.
Tap a BSSID's card to open the Details screen.
BSSID Details
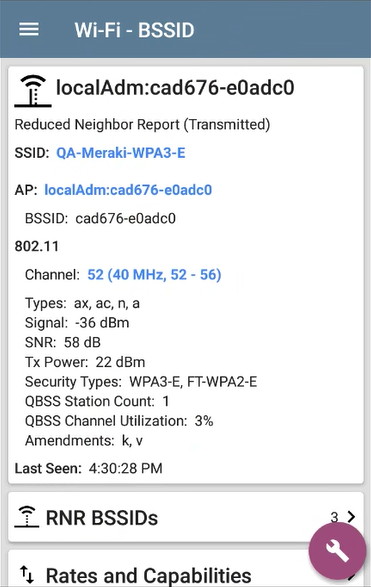
In addition to the characteristics on the BSSID cards, the Details screen displays the following information:
- User-assigned Authorization status (if set)
- Supported 802.11 Types
- Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) measurement
- Network Security type (802.11 Amendment r is indicated by an FT- prefix.
- QBSS station count and channel utilization
- Active 802.11 Amendments (k or v)
- Time activity was Last Seen on the BSSID
BSSID Details also includes cards that link to Rates and Capabilities details, the Wi-Fi Clients list, and BSSID RF and Traffic Statistics details.
Rates and Capabilities
Tap the Rates and Capabilities card to open the full screen.

This screen shows advanced information about the transmit and receive rates and 802.11 capabilities reported by the beacon.
Rates (Mbps)
Country Code
802.11 Capabilities
- BSS Transition amendment (v) status is shown.
- Radio Resource Measurement amendment status is shown.
- 802.11n capabilities are gathered from HT capabilities in the beacon.
- 802.11ac capabilities are gathered from VHT capabilities in the beacon.
- 802.11ax capabilities are gathered from HE capabilities in the beacon.
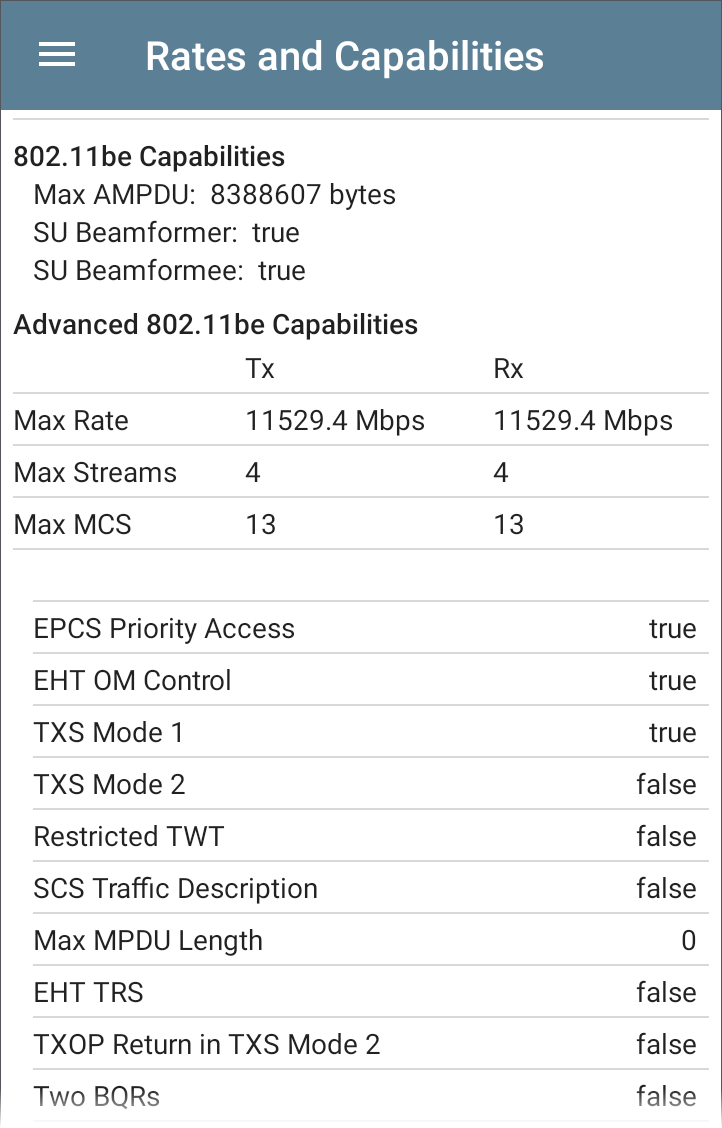
802.11ax and 802.11be Rates and Capabilities
EtherScope nXG can also report Advanced 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) and 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) capabilities detected in the beacon.
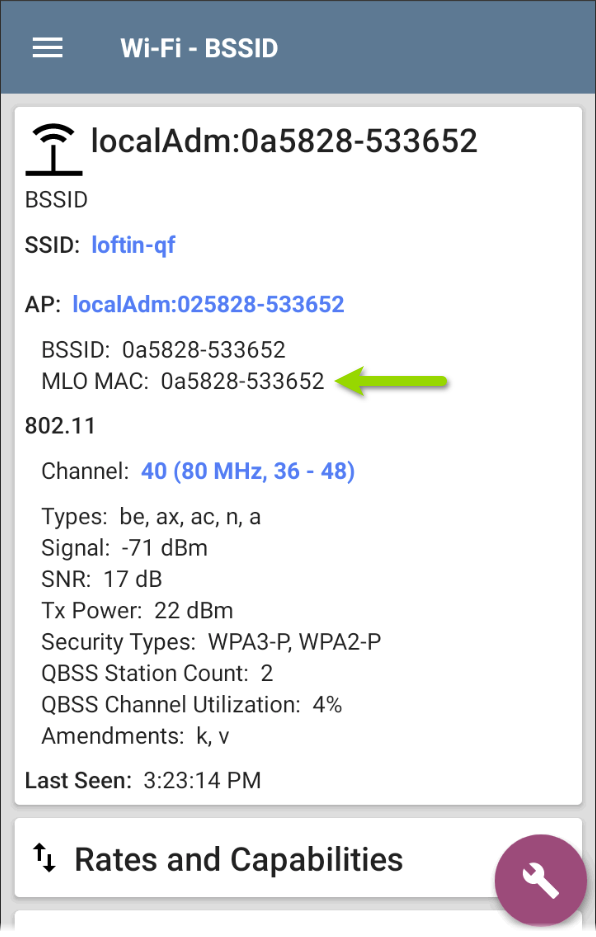
802.11be Multi-Link Operation (MLO)
When an AP includes MLO information in its beacon frames, the Wi-Fi app decodes and displays these parameters. Additionally, the MLO MAC address is displayed on the BSSID details screen.
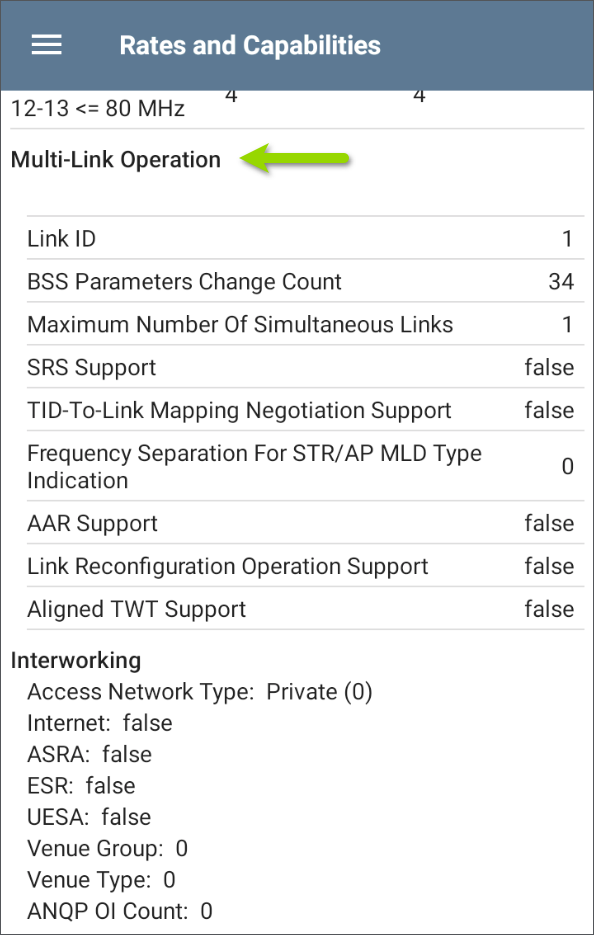
Interworking
EtherScope nXG can also report Interworking information (also known as Passpoint and Hotspot 2.0) detected in the beacon.

Clients
Tap the Clients card to open the Wi-Fi Clients list screen.
BSSID RF and Traffic Statistics
Tap the RF and Traffic Statistics card to open the RF and Traffic Statistics screen. This screen displays the BSSID and channel number at the top of the screen as well as informational graphs.
To pan and zoom on the graphs, you can swipe, double tap, and move the slider under each graph. Tap the Restore icon ![]() to return to the full graph. (See the Trending Graphs topic for an overview of the graph controls.)
to return to the full graph. (See the Trending Graphs topic for an overview of the graph controls.)
See RF and Traffic Statistics Overview in the Wi-Fi Details Screens topic for an explanation of the common elements of this screen.
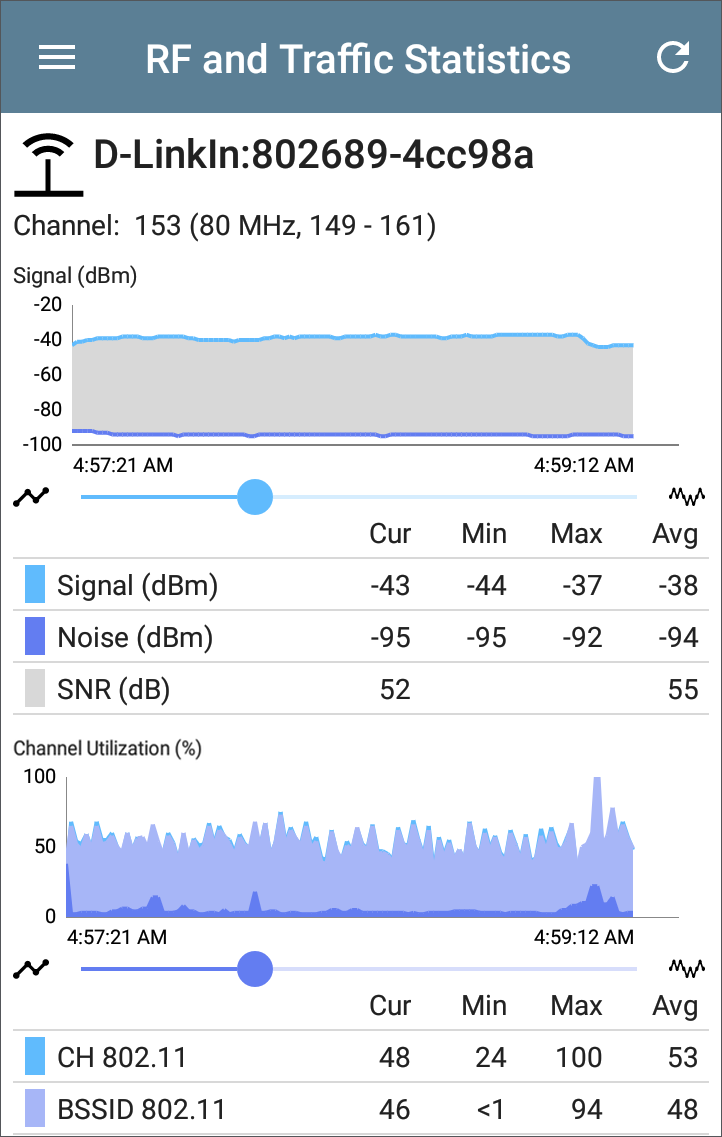
The Signal graph shows the signal in light blue, noise in dark blue, and a calculated SNR.
The Channel Utilization graph uses light blue to show 802.11 channel utilization and dark blue to show non-802.11 utilization:
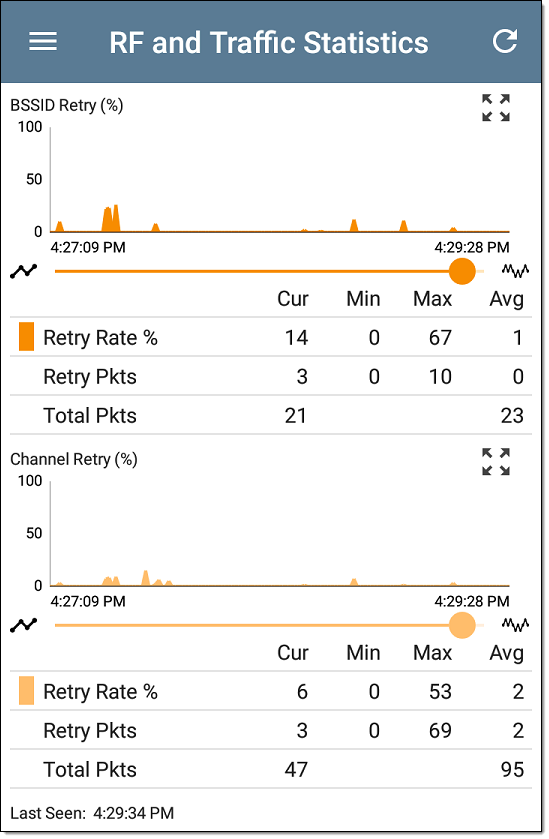
The screen also displays separate graphs for BSSID Retries and Channel Retries:
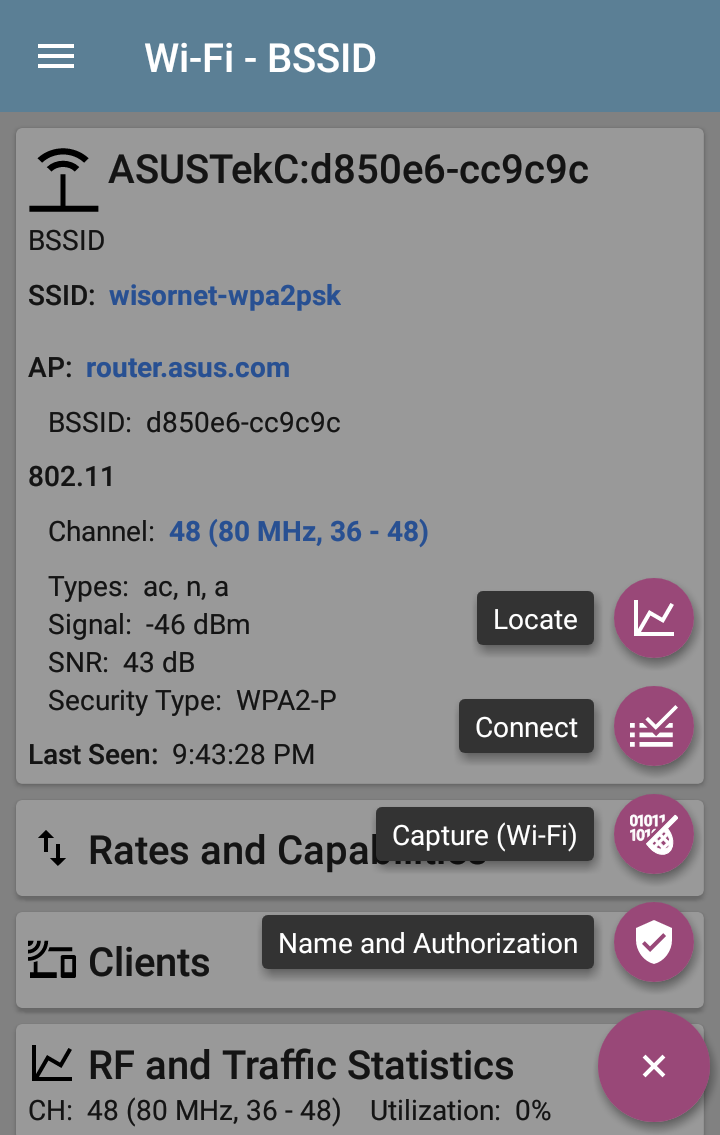
BSSID FAB
The floating action button on the BSSID screen lets you Locate the wireless device, Connect to the BSSID, record a packet Capture of the network traffic with the current BSSID on the connected channel, and assign or change its Name and Authorization.
-
Selecting Locate opens the Locate BSSID screen. See Locating Wi-Fi Devices.
-
Tapping Connect opens the AutoTest app and creates a new Wi-Fi profile called "Connect to [BSSID]." See Creating a Wi-Fi Profile from the Wi-Fi Analysis App in the AutoTest chapter for a more detailed description of this process.
-
Selecting Capture opens the Capture app populated with the Channel and BSSID. See the Capture app chapter.
-
Selecting Name and Authorization opens the Name and Authorization dialog. See Assigning a Name and Authorization to a Device.